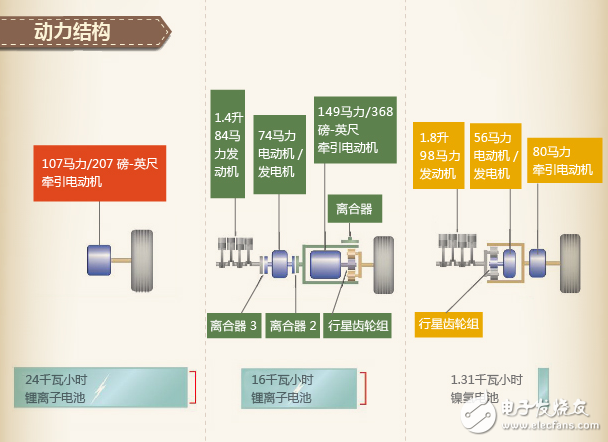
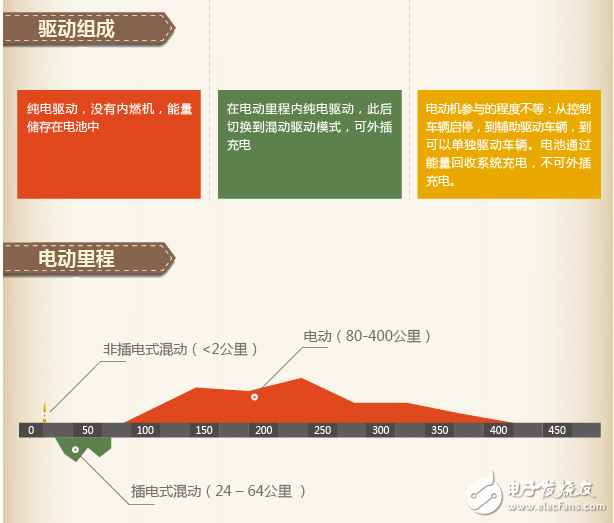
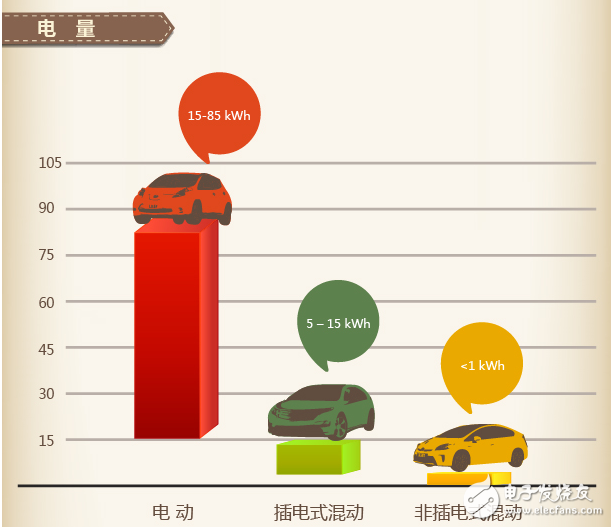
Hybrid vehicles are manufacturers that use hybrid technology to reduce fuel consumption and emissions during start-up, low-speed, and acceleration phases by adding electric motors, allowing the engine to operate in the most efficient area. A hybrid car is a vehicle driven by an engine or an electric motor, so it is inevitably required to refuel. It can usually be driven in pure electric mode, pure oil mode, and hybrid mode. In fact, there is also a general hybrid car, which has a small power battery capacity. For example, the Lexus CT200h has a power battery capacity of 6.5Ah, which is equivalent to some powerful searchlight batteries. Its maximum travel distance is only 3 in pure electric mode. Kilometers. Therefore, the hybrid generally charges the power battery by recovering the kinetic energy during braking, or the generator can be charged by using the excess power of the engine while driving, and there is no trouble that the pure electric vehicle is looking for a "socket" everywhere. A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a new hybrid electric vehicle. Different from the hybrid power of traditional gasoline power and electric drive, the plug-in hybrid drive principle and drive unit are the same as the electric vehicle. The only difference is that the vehicle is equipped with an engine. Conventional hybrid vehicles have low energy density (power battery capacity is generally less than 1.5kwh), so no external charging is required, only the brake recovery kinetic energy is used to charge the power saving battery or the excess power of the engine is used when the vehicle is running at low speed. The generator (motor reversal) charges the power battery. Hybrid electric vehicle is a kind of fuel-saving device. It is a power device mainly composed of steam (chai) oil machine and electric power. The plug-in hybrid vehicle is mainly powered by electric power. After the battery is exhausted, it cannot be charged in time to be powered by a steam (chai) oil machine. 1 Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) can be charged directly from an external power source. The traditional HEV mostly uses the engine to charge the battery and recover the braking energy during the running of the vehicle. 2 Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have large battery capacity and can travel farther by electric power. Electric drives account for a higher proportion of PHEVs, and their dependence on engines is less than that of traditional HEVs. In PHEVs, the motor is mostly the main power output, so it requires high performance of the motor and requires a large capacity battery to provide sufficient power for the motor. The PHEV is mainly powered by electricity. The traditional engine is only used as an auxiliary power, and is only activated when the battery energy is exhausted. The plug-in hybrid can be driven in pure electric mode or in a hybrid mode where the engine and drive motor work together. When driving in the hybrid mode, it works in the same way as an ordinary hybrid vehicle. The drive motor acts as an auxiliary drive mechanism, mainly acting as a “shaving peak and filling valley†to help the engine work in a relatively stable state. Thereby reducing the fuel consumption and emissions of the vehicle. When driving in the pure electric mode, only the battery power supply energy, thereby achieving pure electric drive and zero discharge, so that the external charge is required after the power battery is exhausted, so it is called a plug-in hybrid vehicle. The plug-in hybrid vehicle combines the advantages of the traditional hybrid vehicle, and provides a long range of cruising range (referred to as the hybrid mode) while also meeting the needs of people using pure electric driving, and plays a good role in energy replacement. There are many differences, and the most intuitive one is this. The hybrid car has a small battery capacity and supplies/recovers energy only during start/stop, acceleration/deceleration, and cannot be externally charged, and cannot be driven in pure electric mode; The plug-in hybrid vehicle has a relatively large battery and can be externally charged. It can be driven in pure electric mode. After the battery is exhausted, it is driven in a hybrid mode (mainly internal combustion engine). Plug-in hybrid vehicles are simpler than multiple hybrids and can be externally charged. The motor power should be large enough to ensure that the car can drive at a relatively high speed. The battery capacity is much larger than the hybrid, enough to run for several tens of kilometers in the pure electric mode, and the cruising range is longer (generally 50 km or more). . The integrated fuel consumption of the 100-kilometer hybrid is lower than that of the hybrid. For example, the Prius plug-in version can drive 30 kilometers in the pure electric mode, making the fuel consumption of the 100-kilometers as low as 2L, and about 3L more than the hybrid version (Prius Hybrid and Camry) The hybrid version has a similar fuel consumption). And the charging time is not long, it can be full in a few hours. If you can maintain good charging habits, you can chase the pure electric car with the cost of the car, and you don't have to worry about any battery life. However, due to the larger capacity of the power battery, the increase of the battery pack further increases the selling price, and some regions do not subsidize the insertion and mixing. For example, Beijing only subsidizes pure electricity and does not subsidize the mix. There are very few optional models, two models can be bought for domestic cars, and the BMW 530Le, which has just been listed, is very expensive, so there are fewer options. Method 1: Charging the battery while working on the gasoline engine In addition to the need for a gasoline engine and an electric motor to work in a state of rapid acceleration or uphill, the motor usually stops working when the gasoline engine is working, and the gasoline engine charges the battery. From this diagram, it can be seen that the brown arrow represents the gasoline engine. It will appear, and the green arrow representing the power will flow back into the battery, and charging will begin. Method 2: Braking force charging As with all hybrid models, the energy is reversed into the battery during braking. Whenever the power system is working, as long as the brake pedal is depressed, the green arrow representing the power will reverse into the battery to charge the battery. Method 3: Charging the external power supply This is also the biggest feature of plug-in hybrids different from traditional hybrid models. It can charge the battery through the power plug in life. However, because the battery is not easy to disassemble and carry, it provides all the requirements for the charging field.
Rotary Encoder Wire
Rotary encoder can be used in many fields such as vehicle, industrial automation, industrial robot, elevator and medical. We supply variety of multi-cores shielded signal wire including UL2464, UL2517 and TPU, TPE wire with the properties of excellent bendability, sunlight resistance, cold & heat resistance, oil resistance and high insulation resistance which can perfectly satisfy your needs.
Rotary Encoder Wire,Encoder Wiring Color Code,Encoder Cable,Shielded Encoder Cable Feyvan Electronics Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.fv-cable-assembly.com